There are three types of silicone sealant cracking: cohesive failure, which is manifested as cracking in the middle of the joint; Bond failure, the performance of the joint on both sides of the crack cracking; Mixed failure, the performance of the crack in the middle and both sides of the crack crack at the same time. The following small series for you to explain the causes of sealant cohesive failure and bond failure:
sealantCohesiveness failure usually appears as the middle cracking of the colloids (sealants in the joints are called colloids after curing), because the middle is the thinest and the first to be pulled apart. Reason analysis:
1, with the continuous precipitation of white oil for a long time, resulting in excessive shrinkage, hardness, loss of displacement of the joint gel, unable to adapt to the thermal expansion and cold shrinkage of the substrate displacement resulting in cracking.
2. The amount of crosslinking agent in the formula is low, which is not enough to make the sealant reaction to generate a perfect cross-linking network structure, and there are structural defects, which are easy to lead to colloidal cracking.
3. Sealant is not used within the validity period.
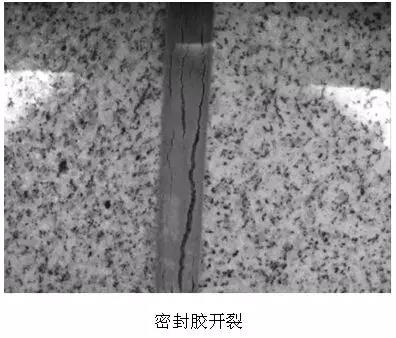
1, the design of the joint is unreasonable, the width of the joint is less than 6mm easy to lead to cracking.
2, the formation of a large number of bubbles in the sizing process is easy to lead to colloidal cracking.
3, the uneven thickness of sizing easy to lead to colloidal cracking in the thin place.
4. When the surface temperature of the substrate is too high or too low, the gel is easy to crack after curing.
5, sealant in the curing process by external force is easy to cause the solidified colloidal cracking.
6, by large external force or substrate deformation, such as earthquake, typhoon, colloid may crack.
7. When the three-side bonding phenomenon occurs, the displacement that the sealant can bear is limited to ± 15% of the original design displacement, which easily leads to the colloidal cracking.
1. The displacement capacity of the selected sealant cannot meet the requirements of joint displacement.
2. The modulus of the selected sealant does not meet the requirements of joints.
3. Bond failure.
Adhesive failure refers to poor bonding between sealant and base material, resulting in poor sealing effect. It usually shows the peeling of the base material and sealant. Reason analysis:
1, the substrate surface cleaning method is inappropriate, cleaning solvent is not appropriate;
2. The surface cleaning of the substrate cannot meet the sealant application requirements, and the surface of the substrate does not volatilize and dry when the sealant is applied;
3. Improper primer or primer has become invalid before use;
4. Excessive primer is applied on the surface of the substrate, and the surface of the substrate does not volatilize and dry when sealant is applied;
5. The sealant in the interface is not fully compacted during the application process;
6. The contact area between the sealant and the base material is too small to ensure the adhesion between the sealant and the base material (the interface design is unreasonable);
7. The sealant is influenced by the outside world during curing, such as wind load, thermal expansion and cold contraction of the base material;
8. During construction, the ambient temperature is lower than 5℃, causing dew condensation and dark dew on the surface of the substrate.

1. The stone curtain wall has not been tested for contamination, so it is impossible to determine whether sealant will contaminate the base material;
2. Acid glue used in metal and stone curtain walls will lead to chemical reaction between the glue and the base material;
2. Acid glue used in metal and stone curtain walls will lead to chemical reaction between the glue and the base material;
4. The adhesiveness between sealant and base material cannot be guaranteed without the compatibility test and bonding test before starting. Chemically incompatible assembly accessories (e.g. seal strip, spacer strip, gasket strip, fixed block, etc.) and sealant contact will cause discoloration or loss of bonding between sealant and substrate.
Previous:Whether the concentration of Dongguan universal glue is proportional to the viscosity
Next:Already the last article
